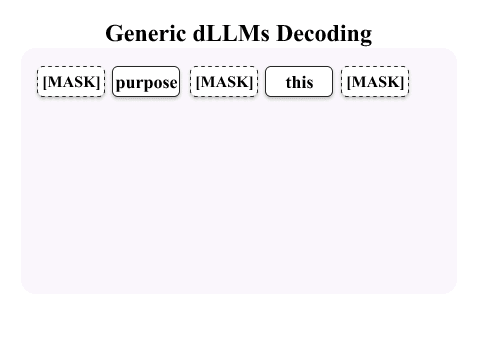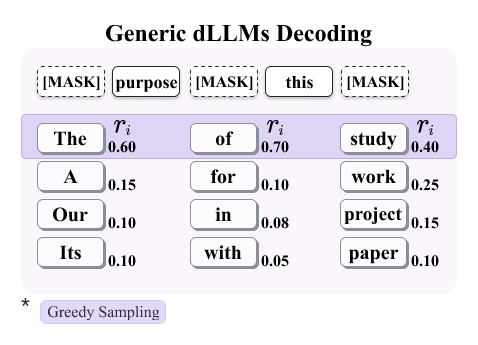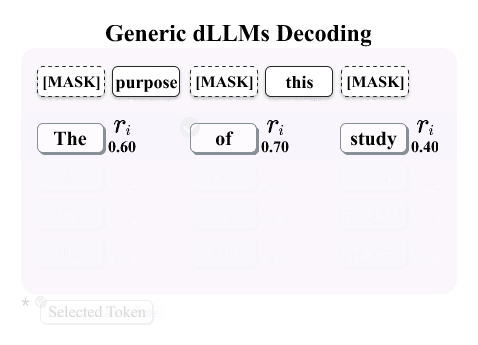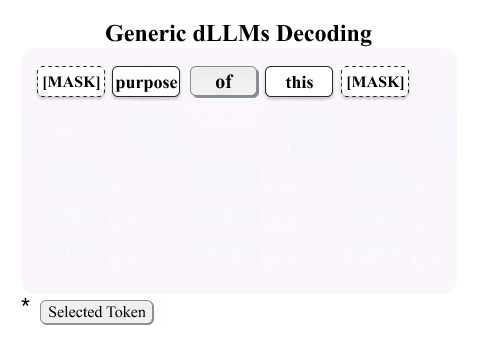
We propose dgMARK, a decoding-guided watermarking method for discrete diffusion language models (dLLMs). Unlike autoregressive models, dLLMs can generate tokens in arbitrary order. While an ideal conditional predictor would be invariant to this order, practical dLLMs exhibit strong sensitivity to the unmasking order, creating a new channel for watermarking.
dgMARK steers the unmasking order toward positions whose high-reward candidate tokens satisfy a simple parity constraint induced by a binary hash, without explicitly reweighting the model's learned probabilities. The method is plug-and-play with common decoding strategies (e.g., confidence, entropy, and margin-based ordering) and can be strengthened with a one-step lookahead variant.
Watermarks are detected via elevated parity-matching statistics, and a sliding-window detector ensures robustness under post-editing operations including insertion, deletion, substitution, and paraphrasing.
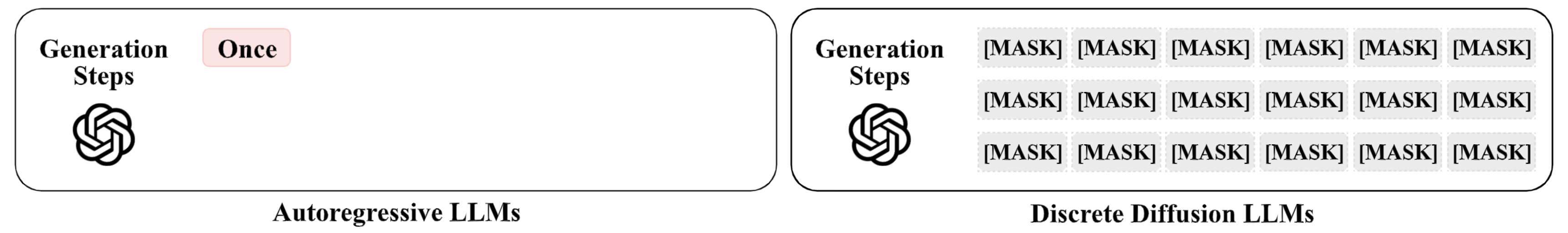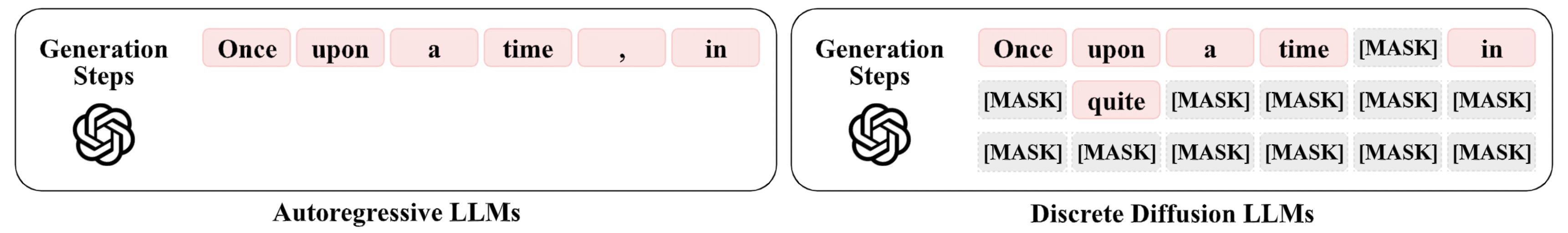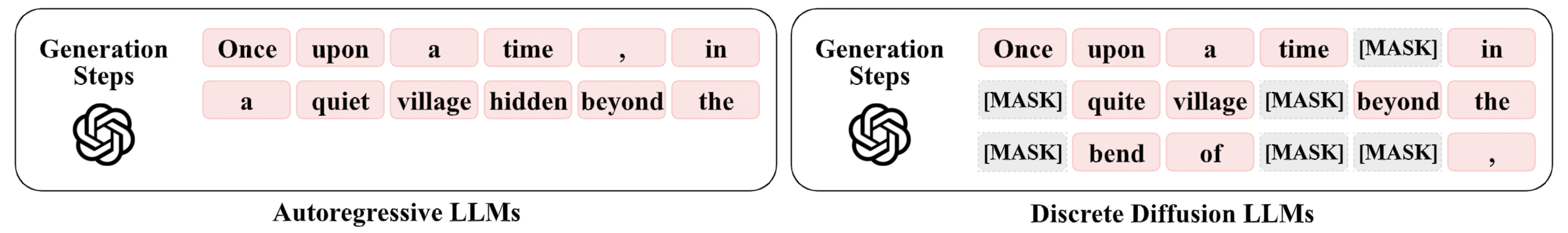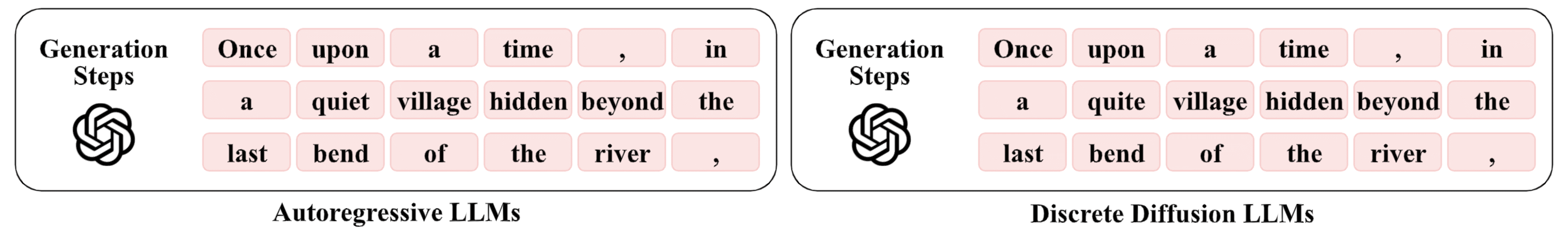
This order-agnostic decoding both creates challenges and opens new opportunities for watermarking. Here, We exploit the decoding order itself as the primary watermarking channel.
The illustration below contrasts three paradigms: existing watermarking schemes, generic dLLMs decoding, and decoding-guided watermarking.


Require: Prompt $x$; output length $n$; predictor $p_\theta$; decoding strategy $\mathcal{F}$
Require: Prompt $x$; output length $n$; predictor $p_\theta$; decoding strategy $\mathcal{F}$; parity matching set $\mathcal{G}_j$
| Method | PPL $\downarrow$ | FPR $\downarrow$ | TNR $\uparrow$ | TPR $\uparrow$ | FNR $\downarrow$ | TPR @ FPR $\uparrow$ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 1% | 0.1% | 0.01% | ||||||
| Greedy Sampling | 4.03 | ||||||||
| KGW ($\delta$ = 1) | 4.33 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.072 | 0.928 | 88.52 | 62.68 | 30.14 | 11.48 |
| KGW ($\delta$ = 2) | 5.02 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.866 | 0.134 | 100.00 | 97.31 | 93.01 | 97.63 |
| KGW ($\delta$ = 3) | 5.83 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.970 | 0.030 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 98.52 | 97.78 |
| PATTERN-MARK ($\delta$ = 1) | 4.11 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 21.76 | 4.17 | 1.39 | 0.00 |
| PATTERN-MARK ($\delta$ = 2) | 4.72 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.040 | 0.960 | 73.50 | 48.50 | 20.50 | 12.00 |
| PATTERN-MARK ($\delta$ = 3) | 5.86 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.584 | 0.416 | 96.26 | 91.59 | 87.38 | 78.97 |
| dgMARK | 4.44 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.540 | 0.460 | 97.86 | 91.98 | 76.47 | 60.96 |
| + 3-beam | 4.75 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.963 | 0.037 | 100.00 | 99.54 | 98.62 | 97.25 |
| + 5-beam | 5.01 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.987 | 0.013 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 99.56 | 98.69 |
| + 8-beam | 5.16 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.991 | 0.008 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 99.12 |
| Multinomial Sampling | 4.21 | ||||||||
| KGW ($\delta$ = 1) | 5.59 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.107 | 0.893 | 89.80 | 60.91 | 32.99 | 14.21 |
| KGW ($\delta$ = 2) | 6.38 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.876 | 0.124 | 99.41 | 98.82 | 97.65 | 91.18 |
| KGW ($\delta$ = 3) | 7.87 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.984 | 0.016 | 100.0 | 99.21 | 99.21 | 98.41 |
| PATTERN-MARK ($\delta$ = 1) | 5.45 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 25.26 | 5.67 | 1.55 | 0.00 |
| PATTERN-MARK ($\delta$ = 2) | 6.33 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.060 | 0.940 | 78.00 | 53.50 | 27.50 | 16.50 |
| PATTERN-MARK ($\delta$ = 3) | 7.69 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.586 | 0.414 | 98.99 | 95.96 | 91.41 | 83.33 |
| dgMARK | 5.27 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.929 | 0.071 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 99.41 | 95.29 |
| + 3-beam | 5.40 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| + 5-beam | 5.76 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| + 8-beam | 6.00 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
Table 1. Empirical results under greedy and multinomial sampling with LLaDA 1.5 on the C4 dataset, reporting perplexity (PPL) and detection metrics. Greedy and multinomial sampling represent the non-watermarked baselines.
| Model | Method | Greedy Sampling | Multinomial Sampling | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMLU (Acc $\uparrow$) |
GSM8K (Acc $\uparrow$) |
HumanEval (Pass@1 $\uparrow$) |
MMLU (Acc $\uparrow$) |
GSM8K (Acc $\uparrow$) |
HumanEval (Pass@1 $\uparrow$) |
||
| LLaDA | Non-watermarked | 0.648 | 0.797 | 0.427 | 0.594 | 0.775 | 0.360 |
| KGW | 0.558 | 0.662 | 0.092 | 0.520 | 0.464 | 0.055 | |
| PATTERN-MARK | 0.570 | 0.635 | 0.134 | 0.532 | 0.438 | 0.073 | |
| dgMARK | 0.647 | 0.787 | 0.280 | 0.588 | 0.735 | 0.226 | |
| dgMARK +3-beam | 0.647 | 0.771 | 0.268 | 0.580 | 0.678 | 0.152 | |
| LLaDA 1.5 | Non-watermarked | 0.650 | 0.821 | 0.400 | 0.601 | 0.808 | 0.348 |
| KGW | 0.567 | 0.726 | 0.104 | 0.536 | 0.582 | 0.092 | |
| PATTERN-MARK | 0.579 | 0.670 | 0.152 | 0.540 | 0.513 | 0.079 | |
| dgMARK | 0.649 | 0.814 | 0.317 | 0.596 | 0.759 | 0.201 | |
| dgMARK +3-beam | 0.649 | 0.774 | 0.207 | 0.588 | 0.723 | 0.134 | |
| Dream | Non-watermarked | 0.700 | 0.800 | 0.427 | 0.630 | 0.789 | 0.420 |
| KGW | 0.558 | 0.661 | 0.287 | 0.523 | 0.444 | 0.134 | |
| PATTERN-MARK | 0.594 | 0.652 | 0.335 | 0.551 | 0.639 | 0.287 | |
| dgMARK | 0.695 | 0.746 | 0.470 | 0.647 | 0.686 | 0.390 | |
| dgMARK +3-beam | 0.695 | 0.701 | 0.342 | 0.636 | 0.648 | 0.262 | |
Table 2. Benchmark results. Results on multiple dLLMs under greedy and multinomial sampling, comparing non-watermarked generation, probability-biasing baselines, and dgMARK (with and without 3-beam search).
@article{hong2026dgmark,
title={dgMARK: Decoding-Guided Watermarking for Diffusion Language Models},
author={Pyo Min Hong and Albert No},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2601.22985},
year={2026}